Challenges to Global Cryptocurrency Adoption
One year after the 2008 global financial meltdown, Nakamoto Satoshi introduced the world to Bitcoin—a new type of digital currency based on blockchain technology.
Bitcoin became the first decentralized currency ever issued. Soon after, Ethereum followed. Since then, the cryptocurrency (crypto) industry has accelerated rapidly and the growth rate more than doubled from 2021 to 2022.
Today, cryptocurrency is being adopted around the globe, and there are more than 16,000 cryptocurrencies in use throughout the world.
Everyday people, large institutions and even governments are beginning to explore the utility of cryptocurrency and its ability to drive a digital revolution in many sectors—especially in finance and business.
Yet, global adoption of crypto has been hindered as there are several obstacles to overcome before digital currency will be accepted as sound money throughout the world.
Barriers to Global Crypto Adoption
Global crypto adoption implies a truly decentralized asset that can be used to securely transfer and store value anywhere in the world.
Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology company, TripleA, estimates that there are now more than 300 million cryptocurrency users across the world.
This remarkable market achievement translates to just 4% of the world's population with ample room for growth. In fact, the global cryptocurrency market is predicted to grow with a compound annual growth rate of 56.4% from 2019 to 2025.
In early 2022, multinational financial services firm, Wells Fargo, compared the rapid global adoption of crypto to that of the internet during the mid-to-late 1990s.
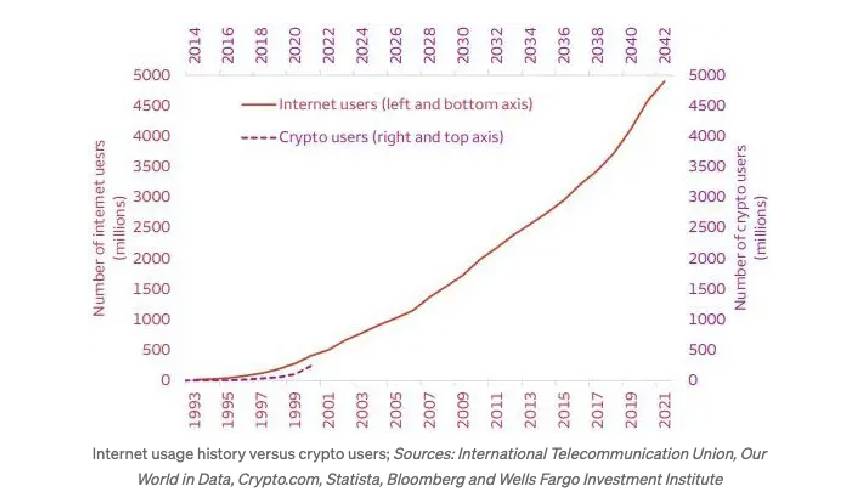
According to the bank’s report:
“…It appears that cryptocurrency use today may even be a little ahead of the mid-to-late 1990s internet. Precise numbers aside, there is no doubt that global cryptocurrency adoption is rising, and could soon hit a hyper-inflection point.”
Nonetheless, in order to scale globally, the industry will need still to overcome several key barriers, including:
(1) Excessive Price Volatility
Once dismissed as a fringe interest of tech evangelists, cryptocurrencies—particularly Bitcoin, which is perhaps the most widely recognized digital currency—have skyrocketed in value in recent years. For instance, the value of Bitcoin hit an all-time high of over $60,000 USD in November 2021.
However, the price of cryptocurrencies can fluctuate wildly. Despite its 2021 high, Bitcoin was trading for well below USD $20,000—a ~66% decrease—by summer 2022.
Since then, the coin has increasingly tracked alongside the stock market as it struggled in the face of high inflation, rising rates, and lower investor confidence.
Some experts say the volatility of cryptocurrencies limits their usefulness as a means of transaction. This makes sense as most buyers and sellers don’t want to accept payment in something whose value can change dramatically from day-to-day.
Still, many believe the price of Bitcoin will eventually surpass USD $100,000 and lead the way for other cryptocurrencies to do the same. This expectation has generated a lot of excitement for the continued adoption of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies by both individuals and institutions.
According to Gartner, by 2024, at least 20% of large enterprises will use digital currencies for payment, stored value or collateral, which has the potential to disrupt current financial networks and business models.
Crypto prices are in part a moving bet which is both a deterrent and part of its appeal. Today, the price volatility is attractive for investors and early adopters who are betting on the industry. But a more mature, stable market will be needed in order to enable mass global adoptions.
(2) Cybersecurity and Theft Risk
Despite its volatility, the adoption of cryptocurrencies has increased dramatically over the past few years because people believe that crypto will become more valuable than fiat currencies in the future.
As such, crypto is just as vulnerable to cybercrime as current digital banking systems, if not more so. As more people invest in cryptocurrency, it becomes easier for hackers to use various methods to steal sensitive data in addition to crypto assets.
Cybersecurity within the world of crypto is a broad and growing topic with multiple strategies available to actively monitor and ensure the security of digital assets.
Although cryptocurrency transactions come with cyber risks, it is possible to protect crypto assets by taking a security-first approach, implementing proper preventive measures and being vigilant about the websites and applications used to store and trade digital assets.
Still, stronger and more consistent security measures will be necessary across the industry to provide users a certain threshold of comfort needed to make global crypto adoption possible.
(3) Uncertain Regulatory Outlook
The driving force behind the blockchain industry is the democratization of technologies and investments.
As such, many governments initially took a hands-off approach to cryptocurrencies. However, the ascent and evolution of crypto, has forced regulators to begin crafting rules for the emerging sector to protect their citizens—especially from scams and fraudulent investments.
Today, regulations vary widely around the world, with some governments embracing cryptocurrencies and others banning them outright.
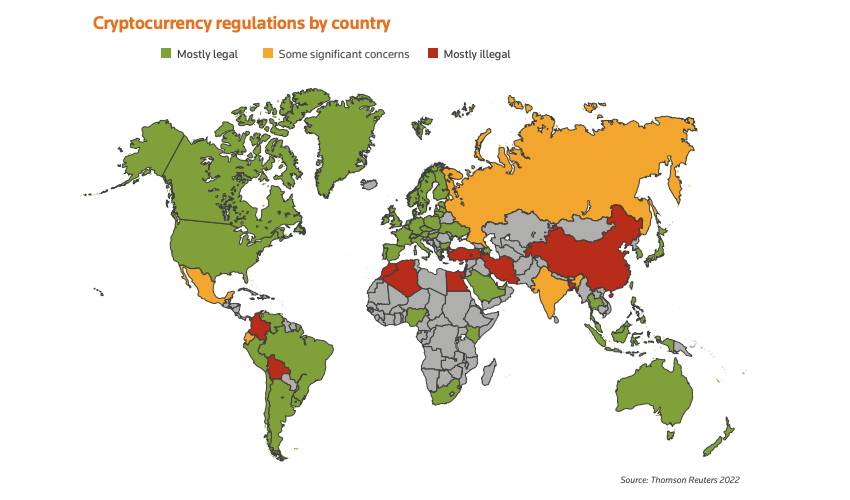
The challenge for regulators is to develop rules that limit traditional financial risks without stifling innovation.
Recently, United States president Joe Biden delivered the first-ever comprehensive framework for responsible development of digital. The executive order focuses on six core areas of cryptocurrency use:
- • Consumer and investor protection
- • Promoting financial stability
- • Countering illicit finance
- • Reinforcing U.S. leadership in the global financial system and economic competitiveness
- • Financial inclusion
- • Advancing responsible innovation
- • Exploring a U.S. Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Many industry experts agree that this could be a turning point in the push for institutional adoption of cryptocurrencies—something many have long called for.
Still, more is needed. Over time, the successful use cases based on cryptocurrencies will directly depend on global regulators and industry professionals working together to promote the adoption of digital assets in everyday life.
Governments will need an agreed upon set of efficient laws to check the crypto industry if wide-scale global adoption is to become a reality.
(4) Energy Use and Environmental Effects
Another significant drawback that has hindered the global adoption of cryptocurrency has been its energy consumption. "Mining" for cryptocurrency is a power-hungry activity, involving heavy computer calculations to verify transactions. For example, Bitcoin was once called out for using more electricity than Argentina, a country of 45 million people.
This is because most of crypto’s energy consumption goes into its Proof of Work (PoW) consensus protocol, which verifies accurate transactions by solving complex equations before adding new transactions. Thus, requiring a lot of energy.
Fortunately, there has been a recent shift to more sustainable energy use.
Ethereum, the second largest cryptocurrency in the world and the hub for Defi services, recently announced an upgrade in its consensus protocol that would significantly cut down its energy use. Ethereum’s upgrade in the Eth Merge 2.0 moved to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus protocol which uses 99% less energy than Proof of work.
When asked about the switch to Proof-of-stake, Ethereum’s founder, Vitalik Buterin had this to say:
“Ironically enough for me, it was realizing that that was an unavoidable tradeoff that made me comfortable with it. It made me realize that this is the weakness, and at the same time, I felt confident that it’s all that there is.”
Furthermore, over time as renewable energy technology improves, cryptocurrencies are expected to become more energy efficient and further reduce the environmental impact of crypto mining.
(5) Lack of Skilled Developers
Companies both large and small are leveraging blockchain—the underlying technology powering cryptocurrencies—to reduce costs, increase trust, and improve the security and traceability of data shared across networks.
However, they face a major challenge to integrate cryptocurrency and other blockchain applications with their legacy system(s). In most cases, the organization will need to completely restructure their previous systems, or design a way to successfully integrate the technologies.
The demand for qualified blockchain and crypto staff to implement or integrate blockchain technology is at an all-time high, but the industry suffers an acute shortage of adequately trained talent to develop and manage the complexity of peer-to-peer networks along with the additional qualification and know-how that cryptocurrency and other blockchain applications demand.
A 2022 study by LinkedIn Corp. and OKX revealed an imbalance in the supply and demand of talent in the global blockchain field, with qualified candidates in short supply. Moreover, the study highlighted that talent tenure is short, turnover is high, and talent flow is mainly within the industry.
This could mean that countries growing their talent pool at a faster rate are likely to see higher adoption of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology overall.
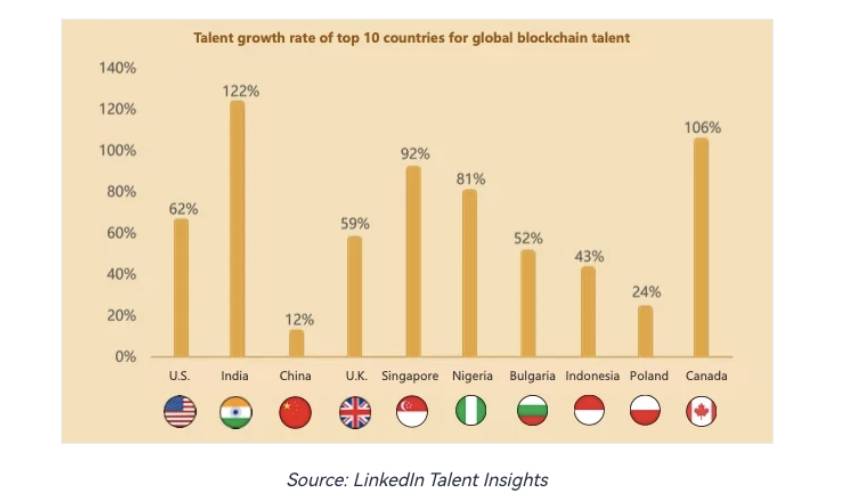
Blockchain technology is in its infancy and is still evolving. It requires time for the developer community to adopt the technology, and for educational institutions to introduce relevant blockchain-related courses. Though this will eventually alleviate the market demand, the results will not be visible for some time.
Due to the lack of skilled developers, organizations do not have access to the necessary pool of blockchain talent to implement and deploy cryptocurrency technology on a global scale.
In Summary
It seems that digital currencies will play a growing role in economic activity and that global crypto adoption is more a question of when it will happen, rather than if it will happen.
The potential uses of cryptocurrencies in corporate, government and financial institutions are overwhelming and are enough for many to continue to push forward despite potential risks.
However, the industry requires significant maturation to address issues of volatility, cyber security, regulation, economic impacts and to build up a qualified talent pool before global adoptions and everyday usage can become a reality.
🌍 Join Us in Making a Difference! 🌱
Do you have innovative ideas, breaking news, groundbreaking research, or expert insights that can help tackle climate change, environmental pollution, and social inequity? Share your voice with the world and be a catalyst for positive change. Together, we can create a better future! Contact us today on publishing@readyplayerinstitute.org.

